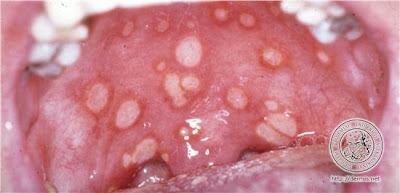


 Sourece : www.dermis.net
Sourece : www.dermis.netI saw a patient in the ward today whom my MO told me that she had ulcers in the mouth and genitalia. One of the diagnosis that came to my mind at that time was this. Common in MRCP PACES part 1 and 2a. Not common in PACES MRCP.
What is the diagnosis ?
What test can be done to support the diagnosis ?
What is the diagnostic criteria ?
What is the treatment ?
Hulusi Behcet was born on Feb 20 1889 in Istanbul. As Professor and Director of Department of Dermatology in Istanbul University, he saw the first case of his disease with oral apthous ulcers, genital ulceration, erythema nodosum and visual loss in 1924. The patient was diagnosed as tuberculosis or syphilis, but his diagnosis was viral infection. He died of heart attack on March 8 1948.
Behcet disease is a recurrent systemic inflammatory disorder of unknown aetiology.
It was first described in 1937 as a triad of recurrent oral ulceration, genital ulceration and uveitis.
Males are more common, usually in the 3rd decade.
Associated with HLA B-51
Common in Turkey, Mediterranean and Japan
Diagnostic criteria - International Study Group for Behcet's Disease 1990
Recurrent oral aphthae - at least 3x in a year
PLUS 2 of
- Genital ulceration - active lesion/scar
- Skin lesion - erythema nodosum, foliculitis, other ulcerations
- Eye involvement - anterior or posterior uveitis, or retinal vasculitis
- positive pathergy test - skin hyperreativity to pin prick( sterile pustule formed in 24 - 48 hours)
Treatment involves Steroids, cyclosporin, cyclophosphamide or azathioprine.
Colchicine may be effective in treating ulceration.

4 comments:
reiters syndrome+++
behcets++
Diagnosis: Behcet disease
Test that can be done: Pathergy test( Does this test stil b carried out?)
Diagnostic criteria:
Oral ulceration plus any 2 others
(Pathergy test, recurrent genital ulcer, Oral ulcer (recurrent),Skin lesions (erythema nodosum, subcutaneous thrombophlebitis etc) and Eye lesions (iridocyclitis, chorioretinitis)
Treatment: Mainly symptomatic with topical steroids
Behcet's disease
Test : Pathergy test (one of the criteria)
Diagnostic criteria (international study group)
Must have 1)Oral apthous ulcers at least 1 year
at least 2 of
1)Recurrent genital ulcers
2)Eye inflammation with loss of vision (e.g iridocyclitis as seen in the picture)
3)Characteristic skin lesions
4)Pathergy test positive
Treatment : Differs depending on presentation.Steroids usually prescribed to control inflammation
Excuse my ignorance but, what is the white circle in the eye of the patient? :$
Post a Comment